Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the production of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This condition is caused by the immune system attacking and destroying the beta cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, resulting in an absolute insulin deficiency within the body. Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, but is more commonly diagnosed in emergencies, such as diabetic ketoacidosis.
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic factors may include a family history of the condition, while environmental triggers, such as viral infections or toxins, may also contribute to the development of type 1 diabetes. People with this condition often have specific autoantibodies in their blood that indicate the immune system is attacking the beta cells.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually develop quickly over a period of weeks or months. Common symptoms include increased thirst and frequent urination, extreme hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing cuts and infections, unexplained weight loss, and nausea and vomiting.
A balanced diet is an important part of managing type 1 diabetes. This includes eating regular meals and snacks, balancing carbohydrates, protein, and fat, counting carbohydrates, limiting processed foods and added sugars, and incorporating fiber-rich foods. People with type 1 diabetes should work with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator to create an individualized meal plan.
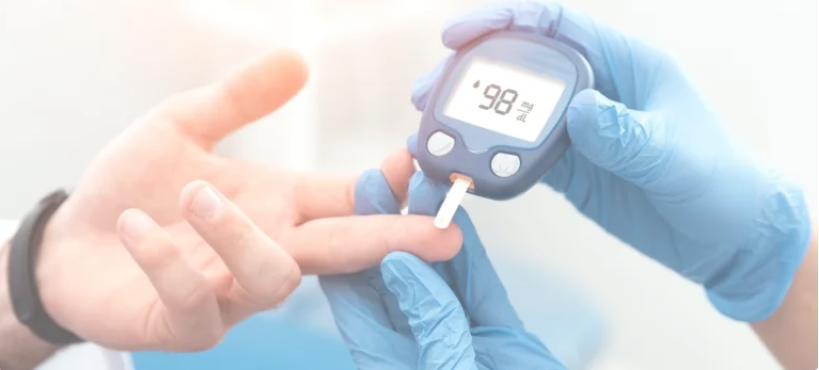
The main treatments for type 1 diabetes include insulin therapy, blood sugar monitoring, healthy eating, physical activity, and regular medical check-ups. While there is currently no cure for type 1 diabetes, ongoing research is aimed at finding new treatments and potential cures for the disease.
People with type 1 diabetes typically have a reduced life expectancy compared to those without the condition. However, with proper management and treatment, many individuals with type 1 diabetes are able to live long, healthy lives. Complications from type 1 diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems, can significantly impact life expectancy if not properly managed.
